Professional
Cost effective
Reliable
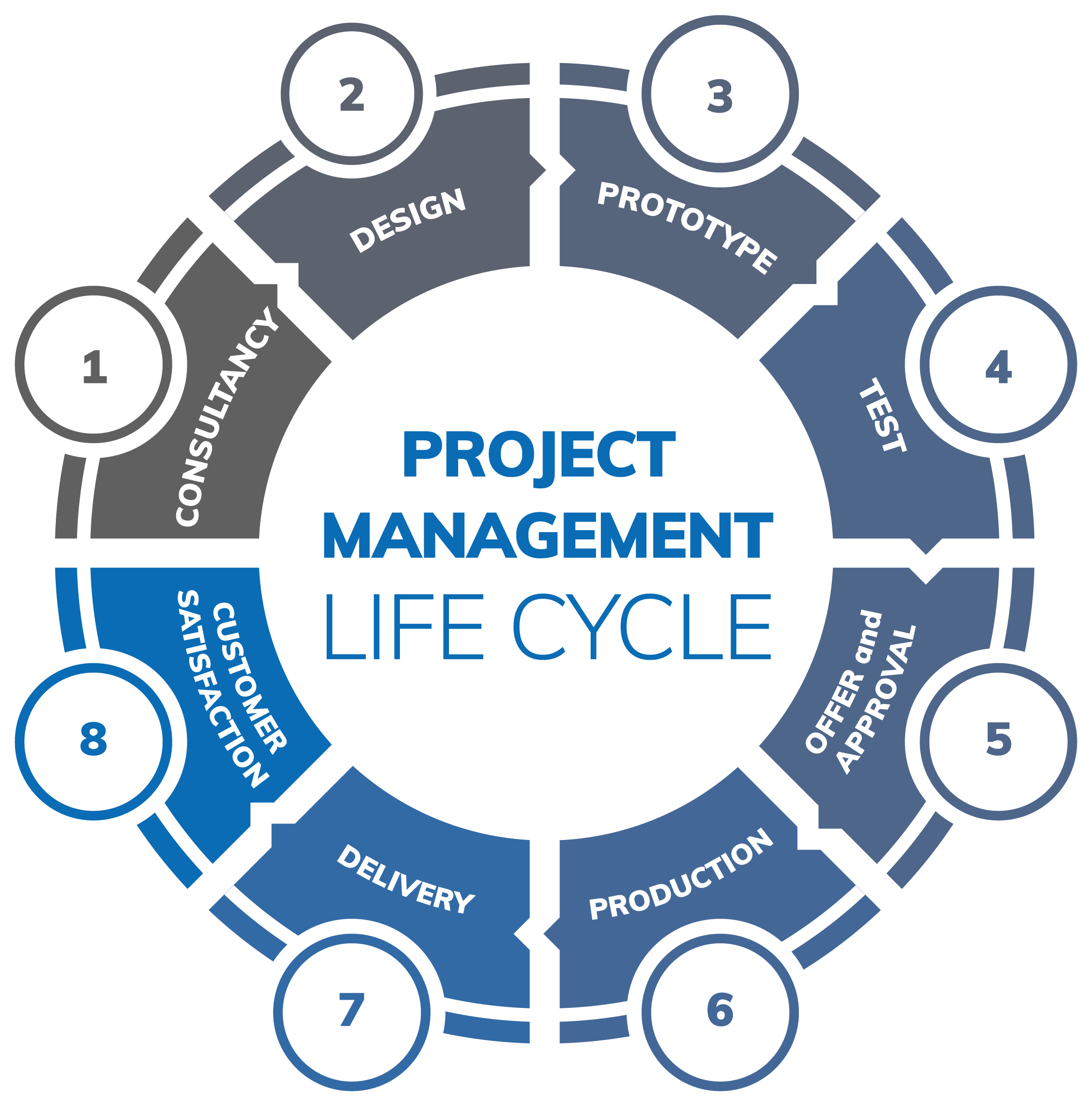
Project Management
Unmatched Project management
Project planning is a discipline addressing how to complete a project in a certain timeframe, usually with defined stages and designated resources. Project management is defined as a collection of proven techniques for proposing, planning, implementing, managing, and evaluating projects, combined with the art of managing people. It is also the application of kn-
owledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet the requirements of a project. Project planning divides the activity into these steps: setting measurable objectives; identifying deliverables; scheduling the planning tasks. Project planning and management is important at every phase of a project. It lays out the basics of a project, including: scope; objectives; goals and schedule.
Key project management concepts
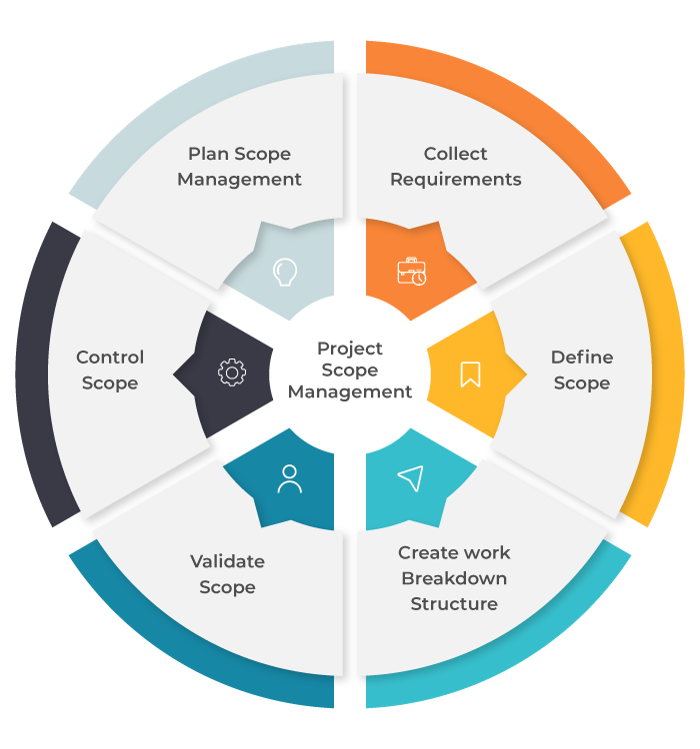
Set the boundaries on your project and define exactly what goals, deadlines, and project deliverables you intend to achieve.

Set up a strategy in order to allocate time to each task and decide on the deadlines for the project phases and delivery dates.
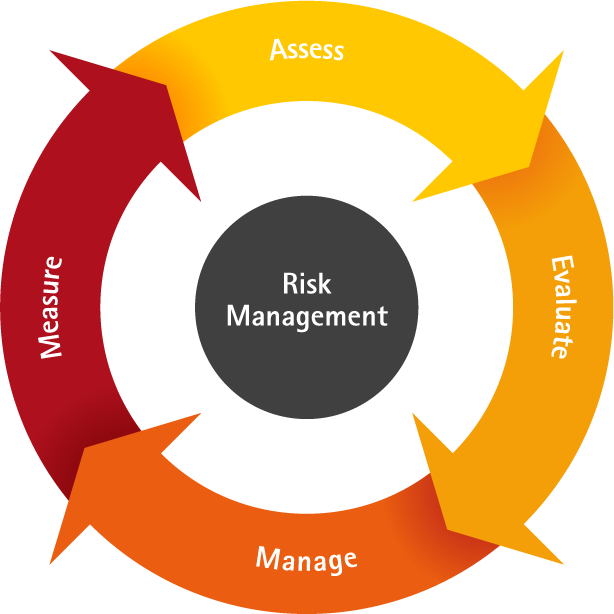
Identify, analyze & respond to any risk that arises over the life cycle of a project to help the project remain on track and meet its goal.
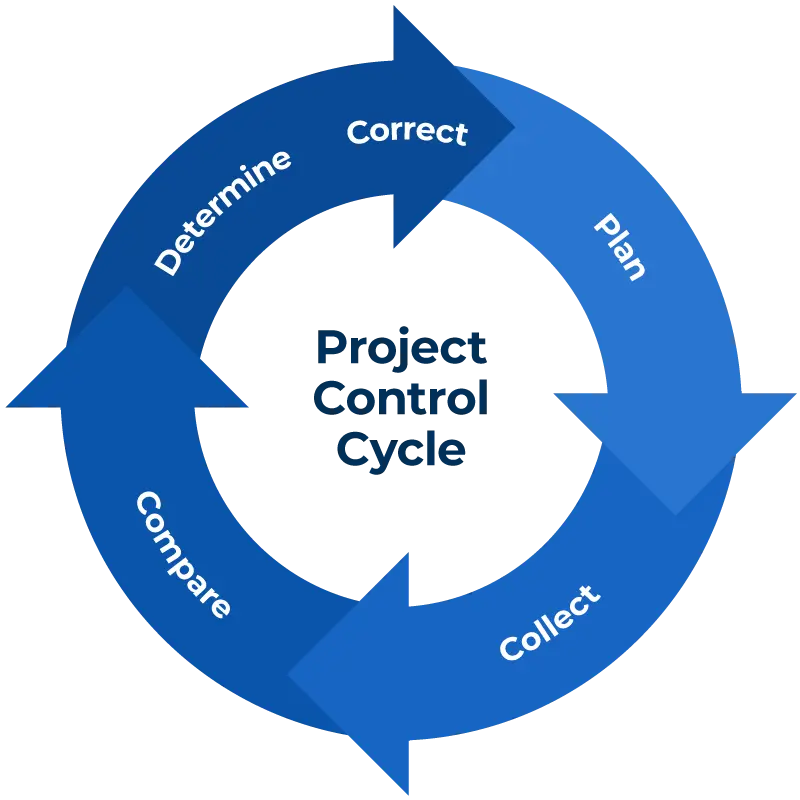
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
In project planning and management, the PDCA cycle is a continuous loop of planning, doing, checking/studying, and acting i.e. carrying out change. PDCA cycle is used when:
- Starting a new improvement during project execution.
- Developing a new or improved design of either a process, product, or service.
- Defining a repetitive work process within a project.
- Planning data collection and analysis in order to verify and prioritize problems or root causes.
- Identifying & implementing any change within a project.
- Working toward continuous project improvement.
1. PLAN
Generate and screen ideas, and develop a robust implementation plan. Be sure to state your success criteria and make them as measurable as possible. Recognize an opportunity and plan a change.
2. DO
Once you’ve identified a potential solution, test it safely with a small-scale pilot project. This will show whether your proposed changes achieve the desired outcome – with minimal disruption to the rest of your operation if they don’t.
3. CHECK
Next, Rrview the test, analyze your pilot project’s results against the criteria that you defined in Step 1, to assess whether your idea was a success. If it wasn’t, return to Step 1. If it was, advance to Step 4.
4. ACT
This is where you implement your solution. But remember that PDCA is a loop, not a process with a beginning and end. Your improved process or product becomes the new baseline, but you continue to look for ways to make it even better.
Project outputs vs. outcomes
Project management terms “outputs” and “outcomes” are used interchangeably but their meaning is different
Project Outputs
Project outputs are defined as what the project produces i.e. the results which are achieved immediately after implementing an activity. Project outputs may be an improved process, installation of a new machine, a benchmarking study, etc. Outputs of the project team process itself may be project plans and supporting documents, status reports, and the like.
Project Outcomes
Outcomes are the effects that the implementation of the project has on the overall organization and should support the strategic direction of an organization. Outcomes may consist of measurable improvements in customer satisfaction, profits or cost containment, improved market position and market penetration, etc. For ease of understanding, outcomes are usually expressed in monetary values.
More details on PPM? get in touch with us!
Project planning and management is crucial in execution of any project. We've in-house robust QC/QA measures to ensure success of any project.