Use of Blockchain in Digitization of Land Records
Introduction
Blockchain (BC) is a decentralized digital ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in a network in a way that ensures the security, transparency, persistency and immutability of the data. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, along with a timestamp as well as transaction data. Hence, once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered without altering all subsequent blocks, which requires the consensus of the network majority. This feature makes blockchain resistant to data tampering and fraud.
All data stored in the blockchain is immutable. Therefore, once a piece of data enters into a blockchain, it is practically impossible to alter or delete its value. In this information age, the Blockchain has changed the business model from centralized to decentralized model of the blockchain. That implies that it can run without any central authority. In fact, it works on Peer to Peer Model rather than Peer-Mediator-Peer. This, therefore makes the process easier, faster, and trustworthy to deal with businesses as it follows Peer to Peer nature.
 Blockchain technology gained prominence in 2009 with the creation of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency. Since then, the blockchain has found applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including land records management, supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and many more. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are another innovation enabled by blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology gained prominence in 2009 with the creation of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency. Since then, the blockchain has found applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including land records management, supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and many more. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are another innovation enabled by blockchain technology.
In land administration and management, blockchain is utilized in the land registry for secure transfer of property (land or houses etc). The concept of smart contracts enables updating of the record automatically; otherwise the ownership is transferred to the buyer through an application form a sit has been. Therefore, with the use of blockchain and smart contracts, the certainty about the ownership of property is assured and guaranteed. This technology often built the trust between parties in transactions as the agreement is implemented and imposed automatically. It also makes the business transactions faster and more organized. Furthermore, it ensures the originality of land records, built the customer’s confidence in the government, it’s more convenient to the customer, hence improves the security of data.
Main Features of Blockchain Technology
In the BC, the nature of work creates a trustworthy platform where users are the owners of the chain. It usually occurs in three phases of the project i.e. pre-construction, construction, and post-construction. In the first stage, the data is collected, gathered, stored and protected. In the second phase the records and data collected is authenticated and secured to prevent illegal access or breaching. In the third stage, all the final changes are recorded in the blockchain model. This forms the basis for further upgrades for the block and a more secure source of information and records for its protection. The blockchain being a distributed ledger, every block in the network has an identical or almost identical copy of the ledger, this further ensures that if a block is compromised or damaged, it can always be restored. Consequently, every block could receive a complete copy of the database from the system through the form of a sub-database. The features of Blockchain that makes it today’s most potential technology include but not limited to the following:
- Persistent: Data recorded cannot be deleted or altered and is saved permanently; hence it can neither be corrupted nor damaged.

- Time-stamped records: The entire data entry in the Blockchain is recoded digitally at the time of occurrence. There is also direct control of the records in BC.
- Approachable: Data records are easily accessible to the participants who can view the data or add it according to consent granted.
- Decentralized: The network is maintained by a group of blocks; therefore, there is no single governing authority. This implies that any data, essential documents, contracts etc can be stored securely and can be directly controlled with the help of the private key.
- Secure: The other features of Blockchain are less likely to breakdown as a direct attack on the whole network of block is difficult for hackers, no involvement of any third-party, no chance of scams, it’s transparent as every change in the Blockchain can be easily monitored, hence enhanced security.
Types of Blockchain Technology
Public Blockchain (PuB): Public blockchains are open and permissionless networks where anyone can participate, read, write, and validate transactions. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. In a PuB, anyone can become a node in the network, and all transactions are transparent and visible to all participants. The consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) are used to validate the transactions and secure the network.
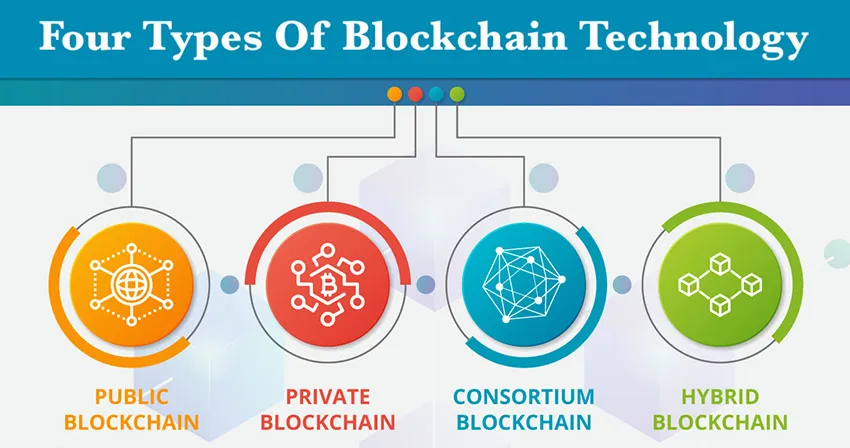 Private Blockchain (PrB): It is also referred to as permissioned BC, members need permission to join the network as transactions are private and are only accessible to the participants. Normally, access and participation are restricted to authorized users only. These networks are typically used within organizations or consortia for specific purposes, such as supply chain management or financial transactions. Unlike PuB, where anyone can join the network, private blockchains require permission from a central authority or administrator to participate. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda.
Private Blockchain (PrB): It is also referred to as permissioned BC, members need permission to join the network as transactions are private and are only accessible to the participants. Normally, access and participation are restricted to authorized users only. These networks are typically used within organizations or consortia for specific purposes, such as supply chain management or financial transactions. Unlike PuB, where anyone can join the network, private blockchains require permission from a central authority or administrator to participate. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda.
Consortium Blockchain (CoB): These are semi-decentralized networks controlled by a group of organizations or entities rather than a single central authority. In a CoB, the consensus process is shared among a predefined set of nodes, often representing different stakeholders in a particular industry or ecosystem. The CoBs offer a balance between the openness of PuBs and the control of PrBs, making them suitable for use cases where multiple parties need to collaborate while maintaining a degree of trust as well as control.
Hybrid Blockchains (HyB): A hybrid blockchain is a fusion of PuBs and PrBs, designed to provide a balance between openness and control. The HyB can be applied to a wide range of use cases, including: Supply Chain Management, Cross-Border Payments, Healthcare Data Sharing, Government Services among others.
Application of Blockchain technology in Land Records
The application of BC technology in land registries has the potential to enhance efficiency, transparency, and security in land administration, leading to improved land governance and socio-economic development. BC is used in land registry for secure transfer of land property. The transparent nature of BC enables to track the changes made in land documents. Its advent in the land registry is playing a very beneficial role in this digital era.
Firstly, it is helping in uplifting the poor, and marginalized section of the society in fighting illegal authorization of land and property transfers. Secondly, the current system for land registration is full of duplicity and inefficiencies, hence land records are not protected. The citizens bear most of these bottlenecks. Similarly, there are thousands of people who face such a crisis across the world. Therefore, with the help of BC, all the records are preserved all the time, are easily accessible, and are fed in the system systematically and permanently.
 The concept of Smart contracts has also gained application in digitization of land records. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain platforms and automatically enforce and execute the terms of the contract when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or brokers, by automating the execution and enforcement of agreements, thereby reducing costs, delays, and the risk of human error or fraud. A smart contract is the legal proof of ownership and contain the history of the property. The buyer is confident that land bought is original and genuine without any duplicity, and that the seller is the lawful owner of the land, which eliminates the probabilities for any future disputes. The adoption and use of smart contracts is gaining momentum and it gears up the procedure of land titling by updating the records automatically.
The concept of Smart contracts has also gained application in digitization of land records. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain platforms and automatically enforce and execute the terms of the contract when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or brokers, by automating the execution and enforcement of agreements, thereby reducing costs, delays, and the risk of human error or fraud. A smart contract is the legal proof of ownership and contain the history of the property. The buyer is confident that land bought is original and genuine without any duplicity, and that the seller is the lawful owner of the land, which eliminates the probabilities for any future disputes. The adoption and use of smart contracts is gaining momentum and it gears up the procedure of land titling by updating the records automatically.
An Example: If the parties that are indulged in the purchase of a given property and have all the correct data at the required time, then the decisions could be made swiftly, hence making the whole process smooth as well as transparent. With the use of BC and smart contract, the certainty about the ownership of property is assured. This technology has built the trust between parties, as transactions is in the form of transparent contract. It makes the business faster and more organized. It improves data security and ensures the originality of the land records. The main merit of using public blockchain technology is the impossibility of making any changes in the blockchain. Thus, it helps in providing a level of trust to the buyers and the sellers.
Land transactions with Smart Contracts
- The land registry in BC, the property owner, can automatically check their property and whether they are eligible to transfer the legal ownership to others or to sell the property.
- The buyer and the seller, both parties, are the user in the blockchain channel and can get easy access to each other, as it connects users over the single platform.
- The banks can also check the status of the current legal ownership of the asset over the blockchain platform before a transaction is executed.
- The verification and validation of property and the land records becomes easily accessible.

- Once the verification gets complete, the users who are buyers and sellers can quickly move to the next process of registration that is the transaction.
- The purchase or sell of land or an asset gets executed by using a smart contract.
- The seller then transfers the property ownership to the buyer.
- The payment process automatically gets completed by transferring the amount from Buyer’s Bank to the seller’s bank.
- Everyone i.e. the buyer, seller, and the bank are able to verify the status of the contract over the blockchain via smart contract platform.
In conclusion, the use of blockchain technology in land transactions makes the process more transparent, secure, efficient, and accessible, whilst also reduces disputes and increases the confidence in land markets. However, it’s important to note that implementing blockchain for land transactions may vary extensively from country to county depending land laws in a specific country. It also requires overcoming myriad of technical, regulatory as well as social predicaments. Nothwithstanding these challenges, the benefits of Blockchain and smart contracts in land transactions outweigh the cost of implemention thereof.













