Introduction
 Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-destructive technique that allows the visualization of structures and features buried underground without the need for excavation. GPRover harnesses ground penetrating radar technology for superior locating and data collection capabilities; integrating advanced subsurface imaging technology with high accuracy GPS and mapping. The antenna’s award-winning triple bandwidth technology also provides a deeper, clearer read of what’s beneath the surface you’re scanning.
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-destructive technique that allows the visualization of structures and features buried underground without the need for excavation. GPRover harnesses ground penetrating radar technology for superior locating and data collection capabilities; integrating advanced subsurface imaging technology with high accuracy GPS and mapping. The antenna’s award-winning triple bandwidth technology also provides a deeper, clearer read of what’s beneath the surface you’re scanning.
Our GPRover unit simplifies the science of utility mapping. Anyone with utility locating knowledge can quickly learn how to operate the GPRover and rely on it to provide accurate underground infrastructure imaging and mapping results. using our suite of radar software solutions, user-created datasets can be stored and shared right from the system’s Windows Getac tablet.
Basic GPR Acquisition Features
 Auto-Calibrate: Using a unique averaging removal algorithm, the antenna and software recognize the prevailing soil conditions and calibrate the images for optimum data gathering.
Auto-Calibrate: Using a unique averaging removal algorithm, the antenna and software recognize the prevailing soil conditions and calibrate the images for optimum data gathering.
Backtrack Feature: Pinpoint the precise location of the target with the position indicator. When a feature is spotted in the data, simply move backward until the indicator is centered on the target.
Time Varying Gain: The only software/hardware integration that recognizes the duration of the pulse and applies gain accordingly. The deeper the target, the higher the gain…automatically!
Position Readout: Simply tap the screen on an image of interest and the distance from the beginning of your pass and the depth will be displayed (x and z coordinates). This feature works both in real time and on stored data being replayed.
Gain Algorithm: Similar to focusing a camera, the operator can increase or decrease gain on a specific depth range. Target identification and layer tracing are much easier for those hard-to-locate targets.
Tagging/Annotation: Features can be identified and highlighted for report building purposes, then positions can be exported to a spreadsheet with either relative positions or latitudes and longitudes.
About the Project
The Kenya Railways Nairobi Central Terminus is a critical transportation hub serving as a central point for rail transport in Nairobi. To ensure the safety and efficiency of rail operations and infrastructure development, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the subsurface conditions. Orbital was contracted by Geomatics Services Ltd. to conduct GPR utility scanning at Nairobi Central Terminus. The GPR survey aimed at identifying and mapping underground utilities to prevent potential conflicts and streamline future construction activities.
Scanning Equipment
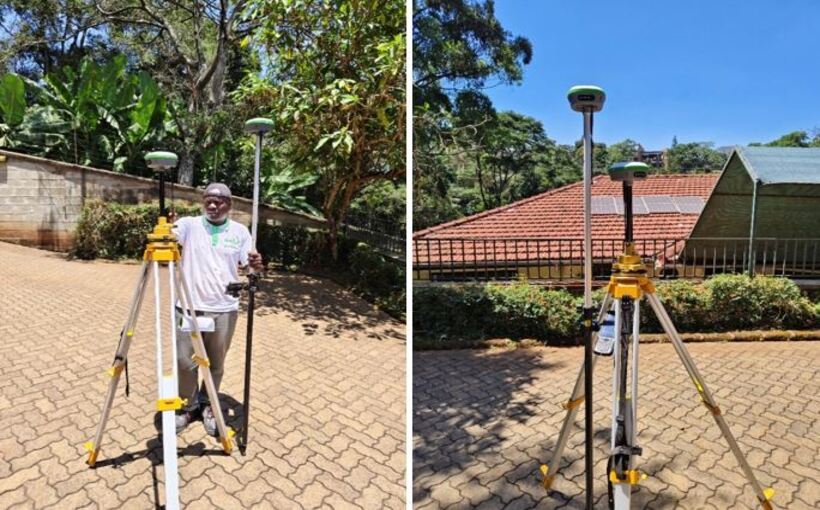
 The Two (2) set of survey equipment were used during this scanning are: USRadar Q5 Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Stonex S800A GNSS receivers i.e. Base and Rover. The USRadar Q5 is a high-performance GPR system designed for subsurface imaging and scanning. The US Radar is a leading innovator of ground penetrating radar (GPR), systems. It offers a wide frequency range and adjustable antennas for various depths of penetration. The Q5 GPR is capable of detecting and imaging underground objects and voids to a depth of 10 metres, making it ideal for underground utility mapping. On the other hand, Stonex S800A GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) machine was utilized to provide accurate positioning data (x,y & z). The aim use was to establish control points and georeference the GPR data for precise mapping.
The Two (2) set of survey equipment were used during this scanning are: USRadar Q5 Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Stonex S800A GNSS receivers i.e. Base and Rover. The USRadar Q5 is a high-performance GPR system designed for subsurface imaging and scanning. The US Radar is a leading innovator of ground penetrating radar (GPR), systems. It offers a wide frequency range and adjustable antennas for various depths of penetration. The Q5 GPR is capable of detecting and imaging underground objects and voids to a depth of 10 metres, making it ideal for underground utility mapping. On the other hand, Stonex S800A GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) machine was utilized to provide accurate positioning data (x,y & z). The aim use was to establish control points and georeference the GPR data for precise mapping.
Project Objectives
- To identify the underground utilities at Nairobi Railways through scanning by the use of GPR equipment.
- To come up with a detailed drawing showing all the scanned underground utilities that appear within the area to be work on.
- To prepare and present project report to the client documenting methodology and outputs of GPR scanning.
Location of Project
The project site is located at Nairobi Railways Station, in Nairobi County. The geographic coordinates of the project site are: [1°17’27.8″S 36°49’42.1″E]. The total area scanned was approximately 5 Acres.
Methodology
The survey was conducted using a grid pattern with 5-meter spacing to ensure comprehensive coverage of the study area. The detailed methodology included the following steps:
 Grid Layout: The study area was divided into a square grid pattern with 5-meter intervals, marked on the ground with survey stakes. The grid is crucial during scanning process as it enforces uniformity and order hence ensuring that the entire project area is scanned.
Grid Layout: The study area was divided into a square grid pattern with 5-meter intervals, marked on the ground with survey stakes. The grid is crucial during scanning process as it enforces uniformity and order hence ensuring that the entire project area is scanned.
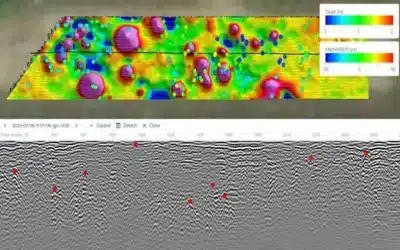
GPR Data Acquisition: The USRadar Q5 GPR fitted with Windows tablet was systematically moved across the grid (i.e. along x and y axes); collecting data at each grid point. The radar emitted electromagnetic waves into the ground, and the reflections were recorded to create subsurface images. In sections where an image depicted an underground utility, the point was then recorded together with its associated coordinates on the tabled installed with GPR field data acquisition software.
GNSS Control Points: The Stonex S800A GNSS machine was used together with the GPR to establish control points and the coordinates of scanned data within the survey area hence accurately georeferencing the GPR data. This process is crucial as it helps during plotting the scanned utilities in AutoCAD Civil 3D.
Data Processing: The collected GPR and GNSS data was downloaded and processed in MS Excel, ArcGIS and AutoCAD Civil 3D to create subsurface images thus plotting them and identifying the potential underground utilities. The classification of the processed data was also done to categorize the utilities into water pipes, sewerlines, electric and telecommunication cables.
Conclusion
 The GPR survey conducted at the Kenya Railways Nairobi Central Terminus using the USRadar Q5 GPR and Stonex S800A GNSS machine provided valuable insights into the subsurface conditions and the nature of utilies at Railway station. It was also possible to scan, collect data, identify, postprocess and classify all the types of underground utilities. The identification of underground utilities will provide data and information which is crucial for future construction, expansion and maintenance of the terminus. The georeferenced GPR data collected during this survey was integrated into ArcGIS database and AutoCAD Civil 3D to create accurate utility maps, allowing for efficient project planning, execution, management as well as risk mitigation.
The GPR survey conducted at the Kenya Railways Nairobi Central Terminus using the USRadar Q5 GPR and Stonex S800A GNSS machine provided valuable insights into the subsurface conditions and the nature of utilies at Railway station. It was also possible to scan, collect data, identify, postprocess and classify all the types of underground utilities. The identification of underground utilities will provide data and information which is crucial for future construction, expansion and maintenance of the terminus. The georeferenced GPR data collected during this survey was integrated into ArcGIS database and AutoCAD Civil 3D to create accurate utility maps, allowing for efficient project planning, execution, management as well as risk mitigation.
Further, with greater depth penetration and resolution than any other locating technology, the USRadar Q5 GPR system can detect anything from fiber optic cables, water pipes, sewerlines to utilities up to 10m deep and everything in between. The three separate datasets generated simultaneously by the triple bandwidth antenna can then be analyzed and cross-compared to create accurate, actionable information for the crew on the job site.
***
Additional GPR Content
 Advanced Algorithms: Operator may enter advanced filtering algorithms, such as Low Pass and High Pass FIR Filters, Remove DC and Peak Envelope, for example.
Advanced Algorithms: Operator may enter advanced filtering algorithms, such as Low Pass and High Pass FIR Filters, Remove DC and Peak Envelope, for example.
Advanced Dielectric Constant Entry: The operator may enter their own values for dielectric constant.
Advanced Depth Calibration: The depth scale can be calibrated based on targets at known depths.
Advanced Attenuation Entry: The operator may enter their own values for attenuation in dB/m.
Signal Loss Calculation: When entering dielectric constant and attenuation, the signal loss is calculated automatically.