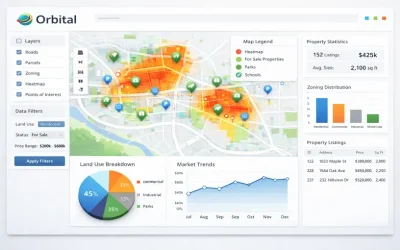
Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Cartography and Remote Sensing Diploma Course is designed to equip students with comprehensive knowledge and practical skills in spatial data analysis, mapping, and earth observation technologies. Below is a detailed overview of the typical course content you can expect from such a diploma program.
1. Introduction to GIS and Remote Sensing
Fundamentals of GIS:
- Definition and components of GIS
- History and evolution of GIS technology
- Overview of GIS applications across various industries
Basics of Remote Sensing
- Introduction to remote sensing concepts
- Types of remote sensing (active vs. passive)
- Overview of remote sensing platforms (satellites, aerial, UAVs)
2. Spatial Data Concepts and Structures
Geospatial data types
- Vector data (points, lines, polygons)
- Raster data (grids, pixels)
Coordinate Systems and Projections
- Understanding latitude and longitude
- Map projections and datum transformations
Data Models and Structures
- Spatial data models
- Topological relationships
3. GIS Software applications
Introduction to GIS software
- What is GIS software?
- Overview of popular GIS software (ArcGIS, QGIS)
Basic operations
- GIS data input and editing
- Map creation and visualization
Advanced GIS functions
- Geo-processing tools
- Spatial analysis and modeling
4. Remote Sensing technologies and image processing
Remote Sensing Sensors
- Optical sensors
- Radar and LiDAR
Image Acquisition and Interpretation
- Satellite imagery sources (Landsat, Sentinel)
- Aerial photography techniques
Image Processing Techniques
- Image enhancement and classification
- Change detection and feature extraction
5. Cartography and Map Design
Principles of Cartography
- Map elements (symbols, scales, legends)
- Design principles for effective maps
Digital Cartography
- Creating digital maps using GIS software
- Interactive and web-based mapping solutions
6. Spatial Analysis and Modeling
Fundamentals of Spatial Analysis
- Buffering, overlay, and spatial joins
- Network analysis and routing
Advanced Spatial Modeling
- Terrain analysis and hydrological modeling
- Predictive GIS modeling and simulation
7. Database Management for GIS
Introduction to Spatial Databases
- Database concepts and management systems (PostGIS, SQL Server)
Data Storage and Retrieval
- Managing spatial data in databases
- Querying and indexing spatial information
Data Integration and Interoperability
- Integrating GIS with other data systems
- Standards and best practices for data sharing
8. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and Data Collection
Basics of GPS Technology:
- How GPS works
- Components of GPS systems
Data Collection Techniques
- Field data collection methods
- Using GPS for spatial data acquisition
Integration with GIS:
- Importing and managing GPS data in GIS software
9. Programming and Scripting for GIS
Introduction to Programming in GIS:
- Basics of programming languages (Python, R)
Automating GIS Tasks:
- Writing scripts for data processing and analysis
Custom GIS Applications:
- Developing custom tools and plugins for GIS software
10. Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing
Environmental Management
- Land use planning, natural resource management
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
- Smart cities, transportation planning
Agriculture and Forestry
- Precision farming, forest monitoring
Disaster Management
- Risk assessment, emergency response planning
11. Project Management and GIS Implementation
Project Planning and Management:
- Stages of GIS project lifecycle
- Resource and time management
GIS Implementation Strategies:
- Organizational considerations
- Case studies of successful GIS implementations
12. Fieldwork and Practical Sessions
Hands-on GIS and Remote Sensing
- Practical exercises using GIS and remote sensing software
Field Data Collection
- Conducting field surveys and data collection
Integration of Field Data with GIS
- Processing and analyzing field-collected data within GIS
13. Diploma Project
Project Proposal
- Student to identify a research project in realms of GIS, survey, cartography etc.
Project Execution
- Applying GIS and remote sensing techniques to solve the problem
Project Presentation and Report
- Documenting findings and presenting project results
14. Recommended Software and Tools
GIS Software
- ArcGIS: Industry-standard GIS software for spatial analysis and mapping
- QGIS: Open-source GIS software for various geospatial tasks
Remote Sensing Software
- ERDAS IMAGINE: Remote sensing image processing
- ENVI: Advanced geospatial analysis and image processing
Programming Languages
- Python: For scripting and automation in GIS
- R: For statistical analysis and spatial data visualization
15. Career opportunities after graduation
Graduates of a GIS and Remote Sensing course can pursue various roles including but not limited to:
- GIS Analyst or Engineer
- Remote Sensing Specialist
- Spatial Data Manager
- A Cartographer
- Environmental Consultant
- Urban Planner
- Agricultural GIS Specialist
- Disaster Management Coordinator
GIS training courses catalogue: Here ++ | E-mail address: [email protected] | WhatsApp No: +254 719 672 296